DES and AES
30 April 2019
Type of attack, preliminary
- 通常會假設攻擊者很強,知道系統密碼的protocol,然後可能有一些plaintext,ciphertext pair
- 而且攻擊者有運算力做key brutal search
- 要符合上述兩點都不被攻破才能算是真正安全的密碼系統
Type of attack
- ciphertext-only attack: 攻擊者只有一堆cipher text
- known-plaintext attack: 攻擊者有一些明文、密文的對照(他eavsdrop使用者輸入的明文跟出來的密文)
- chosen-plaintext attack: 攻擊者能夠選擇特定的plaintext來加密,獲取該密文
- chosen-ciphertext attack: 攻擊者能夠選擇特定的密文來解密,獲取該名文
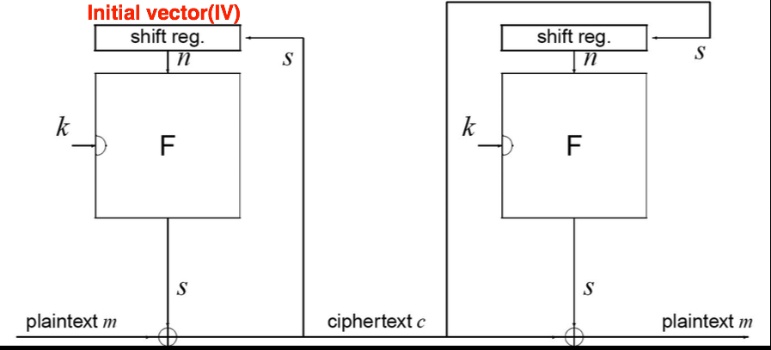
Stream cipher
- 一次對一個byte/bit做運算
- 沒有error propogation
syncrhonous stream cipher
- 執行加密的key stream的產生只跟key stream有關,跟plaintext,ciphertext無關
- sender,receiver壹定要sync好,不然兩邊的keystream不ㄧ樣後面解密全掛
- 沒有error propogation,假設解密運算某個bit錯了,後面的bit解密不會受影響
- 很怕active attack,attacker可以修改ciphertext裡的字元來預期自己想要的輸出,因為沒有diffusion,就是只有明文中對應的那個byte被修改
self-synchronous stream cipher
- 執行加密的key stream的產生跟ciphertext有關,產生的ciphertext會影響後續的key stream
- key stream長度固定
- 有error progpogation,但在key stream長度的錯誤後,後面又會自動修正(這裡指得是加解密的部分,是指說keystream在和ciphertext做運算產生的keys不小心錯了一個bit後,後面產生的key會有部分是錯的,因為ciphertext解密或加密是錯的,影響到後面部分key的生成,但是key stream不變只會影響該長度的bit,等shift register shift完後面就沒事了)
- 有較好的diffusion
Keystream要求
- look random
- unpredictable
- low correlation between key & keystream bit
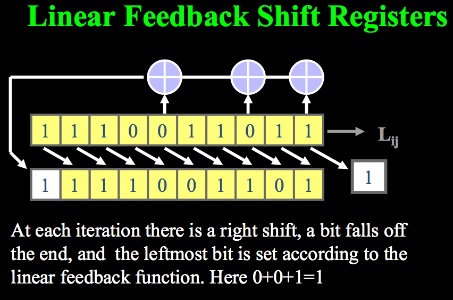
- 大部分keystream是LSFR產生的(linear feedback shift register)
LSFR
RC4
- synchronized stream cipher
- 利用RC4演算法產生keystream,再拿keystream和plaintext xor
Initialize key
$ int S[256] = {0,1,2,3...255}, K[256] = {random 0~255}
$ j = (j+S[i]+K[i])%256
$ swap(S[i],S[j])
Encryption
generate one-byte keystream and xor with plaintext
$ i = (i++)%256 //確保所有陣列每個元素都被用過
$ j = (j+S[i])%256 // 讓output non linear
$ swap(S[i],S[j]) // 確保array會有state變化
$ t = (S[i]+S[j])%256 // 保證output t只能提供很少關於array S的線索
$ Ks = S[t] -- keystream byte
如果i跟Ks都被得知,那攻擊者就能知道S[t],但不會知道S[i],S[j]。
Block cipher
- 一次可以處理64/128 bits
- block要夠大,不然可以dictionary attack(容易搜集足夠的plaintext/ciphertext pair)
- 會把plaintext拆成blocks,拿keystream進行多回合的運算(permutation,substitution),每回合的key也是derive出來的(例如從keystream產生,每回合的key都不一樣)
- 每個回合的運算一定要invertible,不然就不能解密了
Type
- Feistel cipher: 把輸入拆成左右半邊,右半邊在下一個round變成左半邊,左半邊做一堆運算後跑到下一個round
- Substitution-permutation network: 分成多個block,block內元素做substituion,block之間做permutation後得到的在做xor
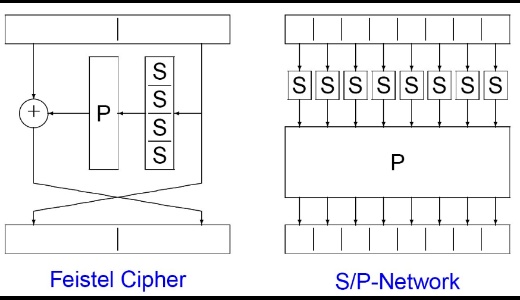
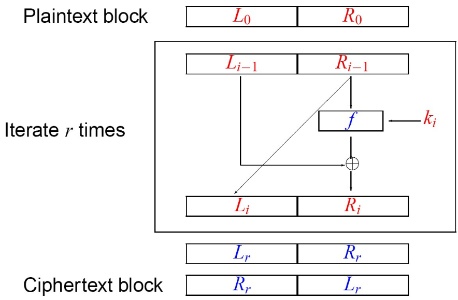
Fiestal network
\(L_i = R_{i-1}\) \(R_i = L_i ^ f(k,R_{i-1})\)
DES
- block size : 64 bits, key size: 56 bits
- 16 rounds of block operation
- different keys for every round, but all of them are derived from a initial keystream
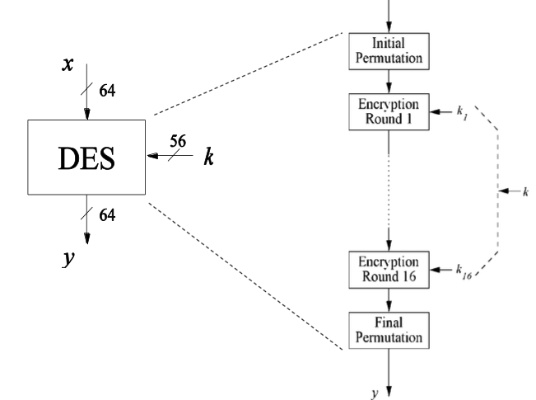
Phase
bitwise-permutation
就permutation,會有一個permutation table,就是做mapping的意思,看數字幾號就換成新的數字
Encryption round
把64bits的block切成左右兩份($L_i,R_i$)
\(L_{i+1} = R_i\)
\(R_{i+1} = L_i xor f(R_{i+1},k_i)\)
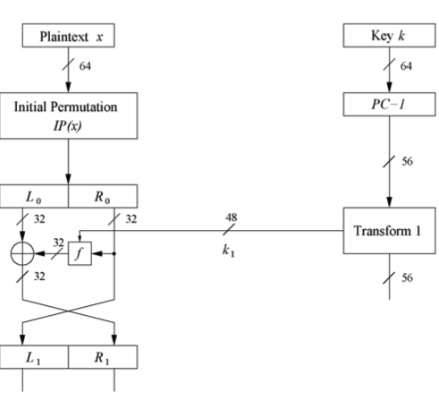
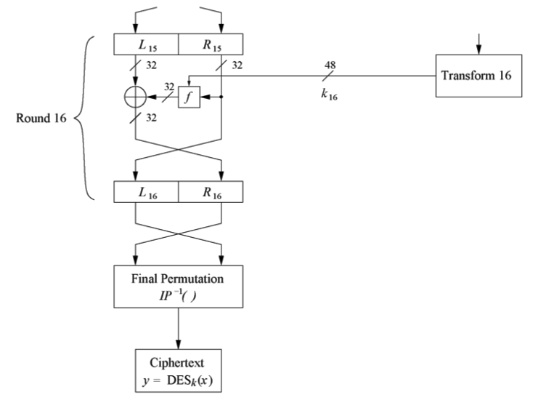
f function
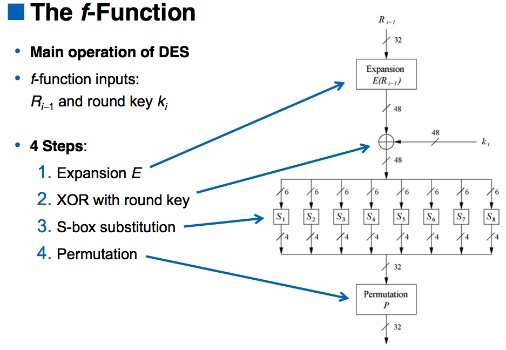
Expansion
做diffusion,把input 32 bits 做diffusion然後變成48 bits輸出
Add round key
把key跟Expansion結果做xor,都是48 bits
S-box substitution
把上述48bits拆成6bits一組,做S-Box的differential, non-linear operation,去看對照表把它換成4bits的輸出
Permutation
就是做permutation
Decryption
同樣的network能繼續用,但是key generation要是reverse order
然後要用R,L的形式傳過去,要相反
\(L_{i-1} \oplus f(k_i,R_{i-1}) \oplus f(k_i,R_{i-1}) = L_{i-1}\)
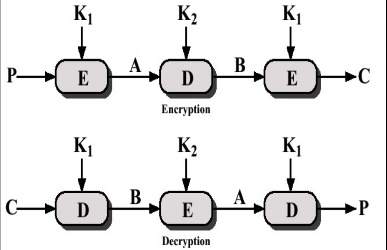
Double DES
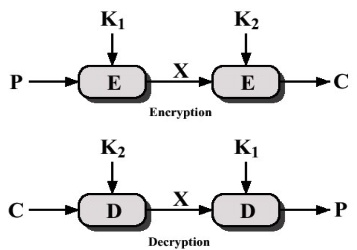
會有Meet in the middle attack
Meet in the middle
假設攻擊者有一堆(P,C) pair 他可以爆搜K1,K2,而且不用花112 bits的安全性,只需要56bits(一半)的安全性就能破解 做法就是他找\(2^{56}\)個K1加密plaintext得到的X集合 再找\(2^{56}\)個K2加密ciphertext得到的X集合,看這兩個的集合有沒有重複的,有的話那個K1,K2就很有可能是Double Des的K1,K2,那他的安全性就跟只有一個DES是一樣的
Triple DES